Table of Contents
Diacritics and Unicode
In RIMMF3, diacritic characters may be entered either as characters or as Unicode code points. Regardless of how they are entered, they are always stored as code points.
The format used by RIMMF for a code point is '\u' followed by a 4-byte code.
For example
Austen, Jane, 1775-1817. Sensibilit\u00E0 e buon senso. Italian
Ugly as they appear, these code points display correctly in any application that understands them (including RIMMF3, after update 150801), and are a standard method of encoding characters in linked data:
Beginning with the 150814 update, RIMMF includes three files of diacritics, with the default being set to the first one:
The rest of this page describes how to use diacritics in RIMMF, and how to create your own custom diacritic file and get RIMMF to recognize it.
Using diacritics in RIMMF
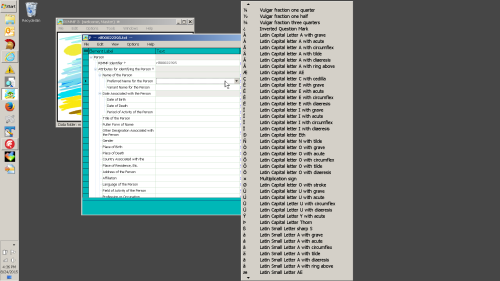
The diacritic menu is popped-up by pressing <Ctrl><Alt>D while editing.
The menu displays along the right edge of the RIMMF 'Text' column and extends in both directions to the edge of the screen (click on the following screenshot for greater detail):
To scroll the list, click on the small up/down arrows at the top/bottom, or mouseover the list and start using the up/down arrows.
As soon as an item in the list is clicked (or <Enter> is pressed), the diacritic character for that item is added to the current cursor position in RIMMF (if applicable) and the list is dismissed.
The list of diacritics is also dismissed as soon as it loses focus.
RIMMF includes an option to display the unicode code point between the diacritic character itself, and the caption, but that option is turned off in the screenshot above (as it makes the menu a bit wider, more cluttered, etc.)
Note that when editing in RIMMF, the first click on a cell places the cursor at the beginning of the field. This is OK if the cell does not contain text, but if it does contain text, click a second time to position the insertion point of the cursor.
Diacritic text files
The diacritics menu is generated by RIMMF from a plain-text file that contains two columns. Each column is required; the columns are separated by one tab.
If your editor supports doing so, it helps to enable 'visible spaces' (Textpad, Editpad, etc.) when you are composing a diacritic text file so that the tabs are visible. Alternately, you could use a program like Excel to create your two columns, and then save the file as tab-delimited text when you are done.
The first column must contain 6 bytes: '\u' followed by the UTF-16 code point in hexadecimal (four bytes). Even if this code can be represented in two bytes, it still must be normalized to four bytes (typically by inserting two zeroes as in the example above).
Then comes the tab character.
The second column contains a human-readable caption or label that describes the code point.
For example,
\u0100 Latin Capital Letter A with macron
Capitalization of the code points is not required:
00c1
is the same as
00C1
But the 'u' in '\u' must be in lowercase.
Capitalization in the caption is up to you.
The order of the code points is also up to you. You may sort them on the code point, as they are in RIMMF, or put the ones most likely to be used first, etc.
Where to save the file
Diacritic text files should be saved to the 'tables' folder in your RIMMF3 directory. If you have the standard installation, this is the folder in your My Documents library; if you have the zip installation, do not put these files in the 'defaults' folder tree, but in the other 'tables' folder.
The program does support diacritic text files located anywhere on your system, and perhaps somewhere in My Documents would also be the best option for a zip installation.
Regardless, be sure to backup your custom files of diacritic characters.
Note
There are many source of Unicode code points on the web.
The official Unicode code charts are themselves available on the web http://unicode.org/charts/
Another good source of this information is wikipedia. Wikipedia presents this information in 'Unicode blocks', a block being a set of contiguous code points. Often, all of the characters for a language will be present in one code block.
Each of the three files of diacritics distributed with RIMMF (listed above) are based on their corresponding Wikipedia pages.
Another good source of this information, especially when searching for a single character, is:
http://www.fileformat.info
1)
Telling RIMMF about your file
Once you have created a file of diacritic code points, the next step is to get RIMMF to recognize it and load it during startup.
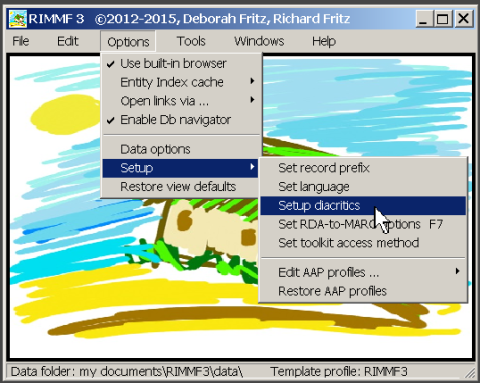
To do this, select 'Setup|Setup Diacritics' from the main Options menu:
This will open the Diacritics support form.
Drag and drop your diacritic text file onto the form. RIMMF will validate the format of the file, and if successful, add it to the list of diacritic files.
Thus, you can install multiple files or versions of diacritics, and RIMMF will maintain a list of all diacritic files that you have added in this way.
When you are using RIMMF and want to switch to a different set of diacritics, go to back to the Options menu, open the Diacritics form.
Select the diacritics file that you want to use from the dropdown menu, then press the 'Activate' button.
RIMMF will load the selected diacritics file and link it into the menu system so that the next time you press <Ctrl><Alt>D, the corresponding diacritics will be displayed.
Whenever the program starts, RIMMF will resume using the last diacritic file selected (if any).